
Http: ///2012/04/hpc-beowulf-style-cluster-using-centos.html I want to check its performance do I downloaded required packages from the internet and copied them in a particular folder. This command returns the complete information for the repository: am having a cluster which is not connected to internet. Now that you have your new repository configured using one of these methods, you should verify that it is configured properly using the yum-config-manager command from earlier to enable and disable PHP sections: # yum-config-manager mysql57-community To see a complete list of repository options, see the man page as follows: $ man yum.conf The first of these lines is the toggle to check for GPG and the second is the location of the key you are checking against: gpgcheck=1
In the last two lines, we configured our information related to GPG. In the first additional option, we configured the toggle enabled, where 0 is disabled and 1 is enabled: enabled=1 We have also configured three more options. In this case, we are using HTTP to access it: baseurl=$basearch/Īs we mentioned, the first three lines are mandatory to configure a repository. The third line is the location ( baseurl) of the repository. The second line in our file is the name we choose to describe the repository: name=MySQL 5.7 Community Server Note: You can have more than section (repository) in a. The first line is the unique identifier for the section and is enclosed in : The first three lines contain the minimum information you need when creating a. Now, let’s discuss the lines we configured. Gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-mysql

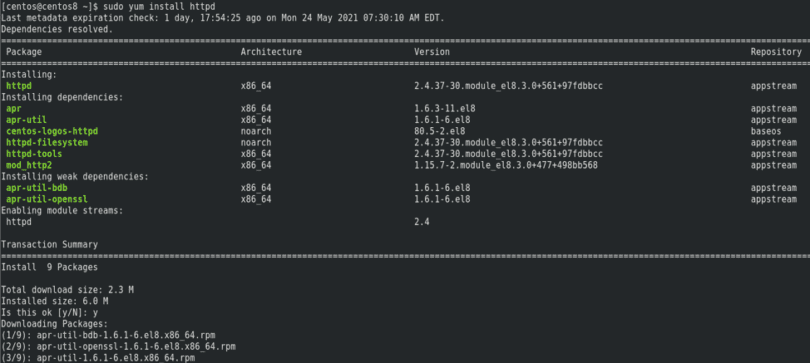
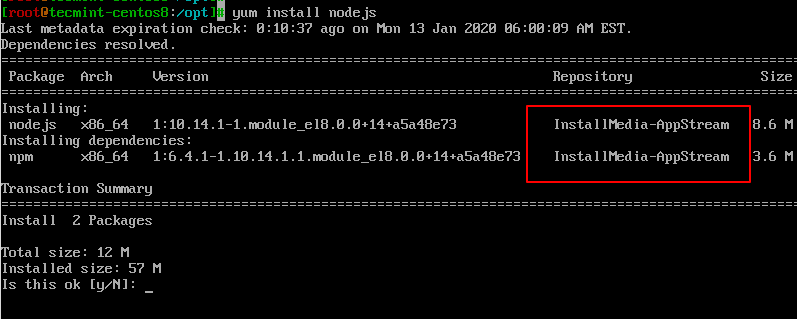
In this example, we will create the repository file for MySQL 5.7: $ nano /etc//mysql57-community.repo repo file within /etc/ using a text editor. The last method of configuring a yum repository manually, where we create a. $ sudo yum-config-manager -enable remi-php72 $ sudo yum-config-manager -disable remi-php54 In the case of needing a specific repository, as in the case of PHP 7.2, you first need to install the repo and then disable and enable repositories using yum-config-manager as follows: $ sudo yum -y install The following command installs the EPEL repository for CentOS 8: # yum install Once you determine which repository you need, there are several different ways to install and enable it. There are also circumstances where you might need to add a lesser-known repository, such as for versions of PHP, or even host your own repository. Or, you might need a specific version of MySQL, which is hosted at. It is always recommended you use a known repository, such as Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux (EPEL), which is hosted at.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
